⚡Introduction to Power Distribution System
**Distribution System** refers to the entire network structure that transmits power from the high-voltage grid (generally 35kV and above), transforms it, distributes it, and **safely and stably transmits it to end-users (residents, enterprises, factories, etc.)**.
I. Main functions of the distribution system
-
Transforms power from the transmission system into a voltage level suitable for use by the consumer
-
Distribution of electricity to various types of users
-
Ensuring the quality of electrical energy (stable voltage, normal frequency)
-
Achieving a safe, economical and reliable power supply
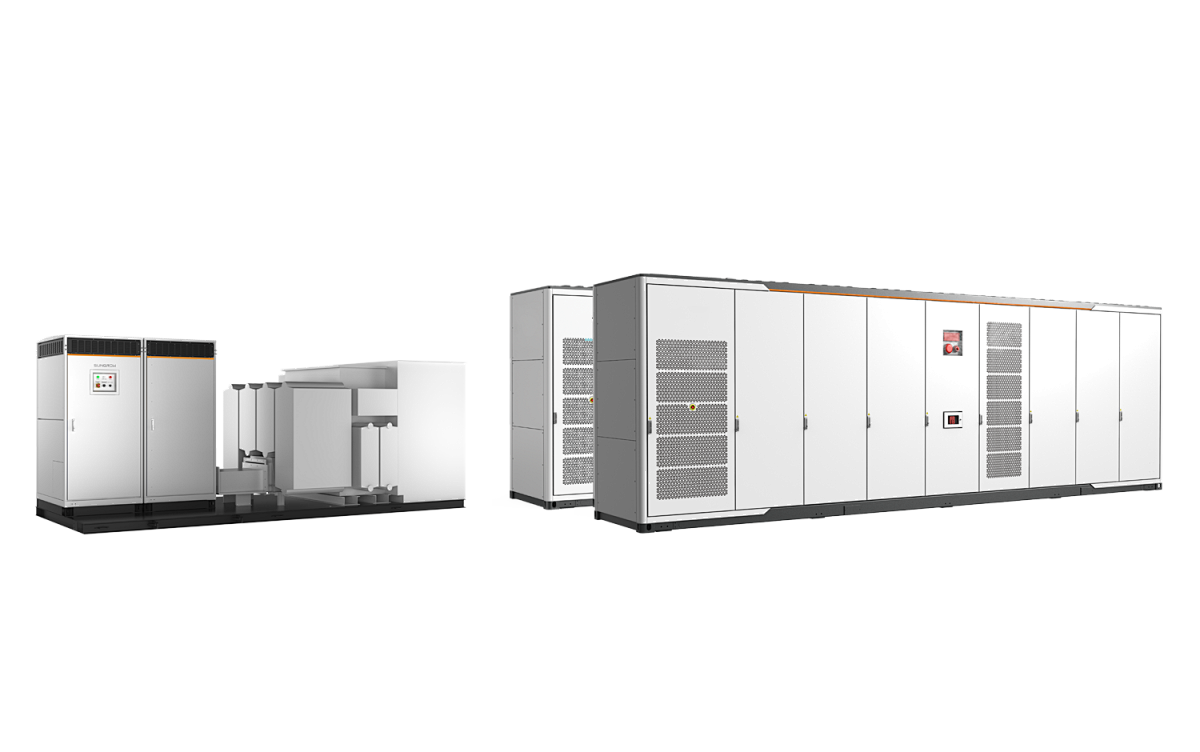
II. Components of the distribution system
| Ingredient | Function Introduction |
|---|---|
| 🔌Distribution transformers | Reduction of transmission voltage (e.g. 35kV) to distribution voltage (e.g. 10kV or 0.4kV) |
| 🧭Power distribution line | Lines for the transmission of electrical energy (overhead lines, underground cables) |
| 🧰Switchgear/Circuit Breakers | Control and protection of grid operation |
| 🏠User access point | Terminal equipment such as user substations, distribution boxes, etc. |
III. Voltage Classification (Typical)
-
High-voltage distribution: 10kV or 6kV for large industrial and commercial users
-
Low-voltage distribution: 400V (three-phase) / 220V (single-phase) for residents, general merchants, etc.
IV. Types of distribution systems
| Typology | Specificities |
|---|---|
| Overhead distribution systems | Low cost and easy to overhaul, but vulnerable to the weather |
| Cable distribution system (underground) | Aesthetics, safety, anti-interference, high cost |
| Open-loop operation closed-loop management | Commonly used in city loop systems to improve power supply reliability |
| Intelligent Distribution System | Integration of IT, automation, remote control for digitalised power distribution |
V. Typical structural diagrams (oral description)
Power plant → Transmission system (220kV/110kV) → Substation → Distribution transformer (down to 10kV/0.4kV) → Distribution line → Various users
VI. Development trends
✅ Upgrading to intelligence, automation and visualisation
✅ Supports access to distributed power sources (e.g. photovoltaic), energy storage, electric vehicles
✅ Emphasis on power supply reliability and energy efficiency optimisation
✅ Combining IoT, 5G and big data to realise smart distribution grids